Theory U: Leading From the Future As It Emerges
This blog is from the Presencing Institute, whose co-founder, Otto Scharmer, joined Maureen for a podcast, The Essentials of Theory U, as part of the International Leadership Association Conference.
(Cambridge, MA: Society for Organizational Learning, SoL, 2007)
Using his experience working with some of the world’s most accomplished leaders and innovators, Otto Scharmer shows in Theory U how groups and organizations can develop seven leadership capacities in order to create a future that would not otherwise be possible.
Tapping Our Collective Capacity
We live in a time of massive institutional failure, collectively creating results that nobody wants. Climate change. AIDS. Hunger. Poverty. Violence. Terrorism. Destruction of communities, nature, life—the foundations of our social, economic, ecological, and spiritual well-being. This time calls for a new consciousness and a new collective leadership capacity to meet challenges in a more conscious, intentional, and strategic way. The development of such a capacity would allow us to create a future of greater possibilities.
Illuminating the Blind Spot
Why do our attempts to deal with the challenges of our time so often fail? Why are we stuck in so many quagmires today? The cause of our collective failure is that we are blind to the deeper dimension of leadership and transformational change. This “blind spot” exists not only in our collective leadership but also in our everyday social interactions. We are blind to the source dimension from which effective leadership and social action come into being. We know a great deal about what leaders do and how they do it. But we know very little about the inner place, the source from which they operate. And it is this source that “Theory U” attempts to explore.
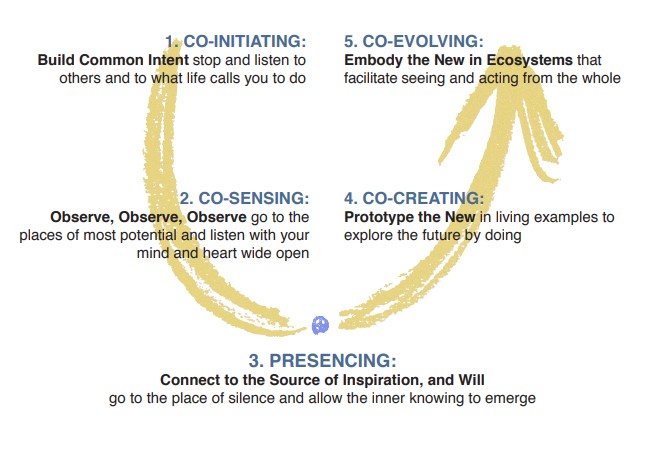
The U: One Process, Five Movements
When leaders develop the capacity to come near to that source, they experience the future as if it were “wanting to be born”— an experience called “presencing.” That experience often carries with it ideas for meeting challenges and for bringing into being an otherwise impossible future. Theory U shows how that capacity for presencing can be developed.
Presencing is a journey with five movements:
As the diagram illustrates, we move down one side of the U (connecting us to the world that is outside of our institutional bubble) to the bottom of the U (connecting us to the world that emerges from within) and up the other side of the U (bringing forth the new into the world).
On that journey, at the bottom of the U, lies an inner gate that requires us to drop everything that isn’t essential. This process of letting-go (of our old ego and self) and letting-come (our highest future possibility: our Self) establishes a subtle connection to a deeper source of knowing. The essence of presencing is that these two selves—our current self and our best future Self—meet at the bottom of the U and begin to listen and resonate with each other.
Once a group crosses this threshold, nothing remains the same. Individual members and the group as a whole begin to operate with a heightened level of energy and sense of future possibility. Often they then begin to function as an intentional vehicle for an emerging future.
Seven Theory U Leadership Capacities
The journey through the U develops seven essential leadership capacities.
- Holding the space of listening
The foundational capacity of the U is listening. Listening to others. Listening to oneself. And listening to what emerges from the collective. Effective listening requires the creation of open space in which others can contribute to the whole. - Observing
The capacity to suspend the “voice of judgment” is key to moving from projection to true observation. - Sensing
The preparation for the experience at the bottom of the U—presencing—requires the tuning of three instruments: the open mind, the open heart, and the open will. This opening process is not passive but an active “sensing” together as a group. While an open heart allows us to see a situation from the whole, the open will enables us to begin to act from the emerging whole. - Presencing
The capacity to connect to the deepest source of self and will allows the future to emerge from the whole rather than from a smaller part or special interest group. - Crystalizing
When a small group of key persons commits itself to the purpose and outcomes of a project, the power of their intention creates an energy field that attracts people, opportunities, and resources that make things happen. This core group functions as a vehicle for the whole to manifest. - Prototyping
Moving down the left side of the U requires the group to open up and deal with the resistance of thought, emotion, and will; moving up the right side requires the integration of thinking, feeling, and will in the context of practical applications and learning by doing. - Performing
A prominent violinist once said that he couldn’t simply play his violin in Chartres cathedral; he had to “play” the entire space, what he called the “macro violin,” in order to do justice to both the space and the music. Likewise, organizations need to perform at this macro level: they need to convene the right sets of players (frontline people who are connected through the same value chain) and to engage a social technology that allows a multi-stakeholder gathering to shift from debating to co-creating the new.
Theory U Encourages You to Step into the Emerging Future.
Examples of these seven Theory U leadership capacities can be found in a number of multi-stakeholder innovations and corporate applications. The Presencing Institute is dedicated to developing these new social technologies by integrating science, consciousness, and profound social change methodologies.
For more information: www.presencing.com
For a 17 page Executive Summary of the Theory U book, go to www.theoryU.com where you can download a pdf file and print it yourself. Or you can request a free copy, as a small printed and bound booklet, to be mailed to you.
About the Author
This article is from the Presencing Institute. Otto Scharmer is a Senior Lecturer at MIT and co-founder of the Presencing Institute. He introduced the concept of “presencing”—learning from the emerging future—in his bestselling books Theory U and Presence. Otto is co-author of Leading from the Emerging Future. His most recent book, The Essentials of Theory U, outlines the core principles and applications of awareness-based systems change.
CC License by the Presencing Institute – Otto Scharmer https://www.presencing.org/resource/permission.
Photo by Dylan Gillis on Unsplash